How AI Helps Us See More: Results of Evaluating the Hiveomics Malignancy Index Among Radiology Residents
The assessment of solitary pulmonary nodules remains one of the most challenging tasks in thoracic imaging. This is especially true for radiology residents, who do not always have immediate access to a senior expert opinion. A new study conducted in collaboration between South Ural State Medical University and Hiveomics demonstrated how the integration of the automated Hiveomics Malignancy Index influences diagnostic decision-making among trainees when interpreting chest CT scans.
Why It Matters
Diagnostic errors in lung nodule assessment often fall into two critical categories:
- Overdiagnosis — benign nodules mistakenly interpreted as malignant, leading to unnecessary invasive procedures.
- Underdiagnosis — malignant nodules overlooked, delaying essential treatment.
Study Overview
A two-phase study was conducted at South Ural State Medical University. The dataset included 100 chest CT scans from adult patients with solitary pulmonary nodules measuring 8–30 mm.
Four radiology residents interpreted all cases first without AI support and then with access to the Hiveomics Malignancy Index (a 5-tier malignancy risk scale). Final diagnoses were confirmed through histopathology, microbiology, or clinical follow-up. The primary outcomes included overall accuracy, pathology-specific accuracy, and over-/underdiagnosis of malignant nodules and tuberculosis.
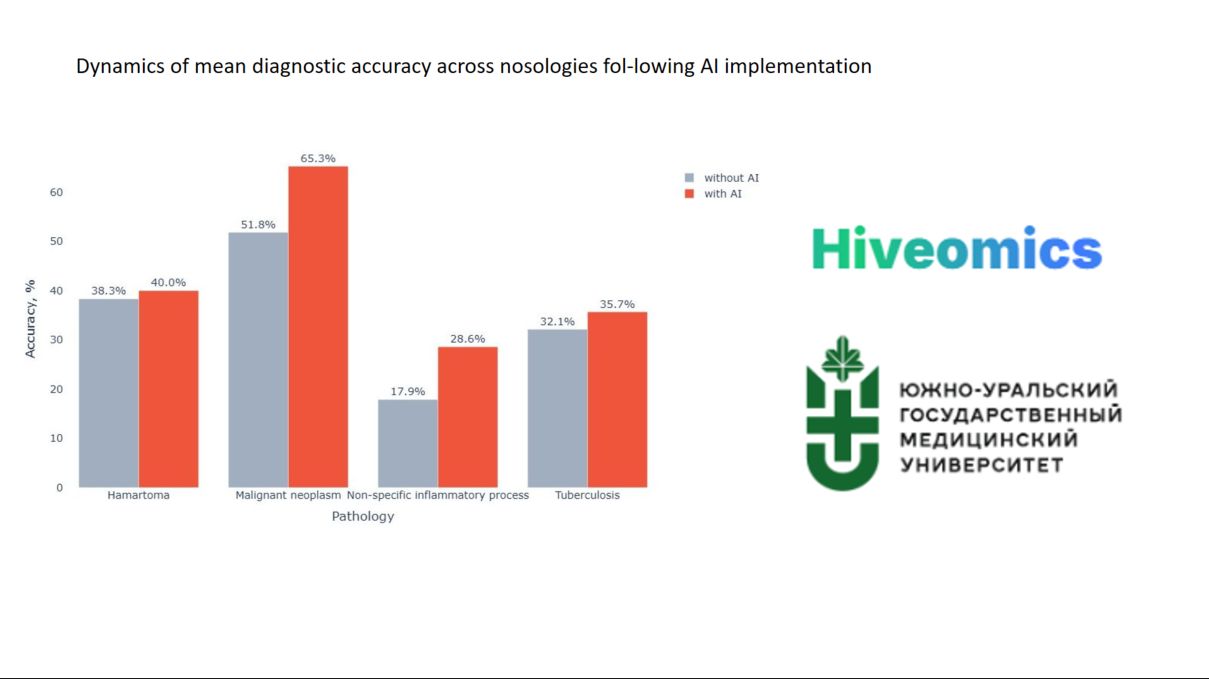
Without AI support, the residents' overall diagnostic accuracy reached only 43%. The greatest difficulties arose in distinguishing malignant from benign processes such as hamartoma, nonspecific inflammatory disease, and tuberculosis.
What Changed With Hiveomics
After incorporating automated analysis, diagnostic performance improved significantly (p=0.0003):
- Overall accuracy increased by 8.8%
- Accuracy for malignant nodules improved by 13.4%
- Overdiagnosis of malignant lesions decreased by 7.1 percentage points
These results show that AI became not just an auxiliary tool but a meaningful mechanism for improving diagnostic quality, enabling residents to make more confident decisions in clinically uncertain situations.
Where AI Helps the Most
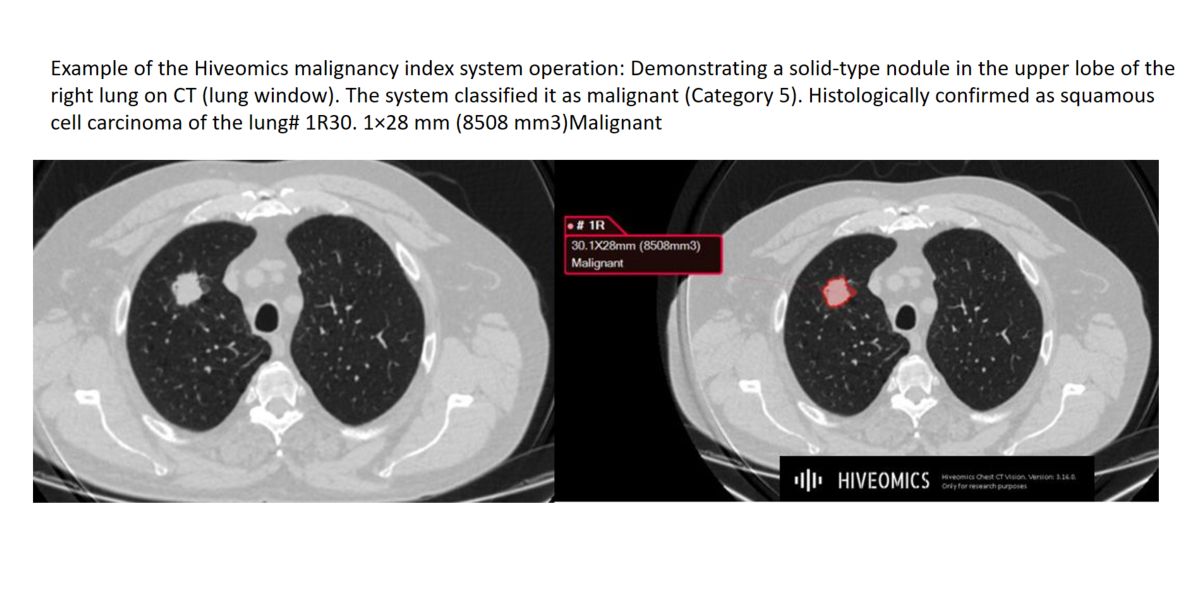
The system demonstrated the greatest effectiveness in tasks where diagnostic precision is crucial — identifying malignant nodules.
At the same time, tuberculosis and several benign processes still require additional algorithmic refinement — a direction that is already being actively developed.
Key Takeaway
Collaboration between a physician and an intelligent analytical system enhances CT interpretation accuracy, reduces the number of critical diagnostic errors, and supports more reliable differential diagnosis. The findings confirm that integrating AI into clinical workflows improves decision-making even among less experienced specialists, ultimately increasing patient safety.
Hiveomics continues to advance its automated lung nodule analysis technologies to make diagnostic processes even more accurate, transparent, and predictable.
See the full study published: http://med-alyans.ru/index.php/Hahn/article/view/1071/1270